If you’ve been playing futsal for a while, you might have heard phrases like “Spread the ball to the weak side” or “Build up the strong side”.
To conclude, the side that is advantageous for a team is commonly called the strong side, and the disadvantageous side is called the weak side.
However, what is considered advantageous or disadvantageous is subjective to the team, so it cannot be strictly defined.
This article explains important concepts when considering the strong and weak sides, namely positional play and the three advantages.
What are the three advantages?
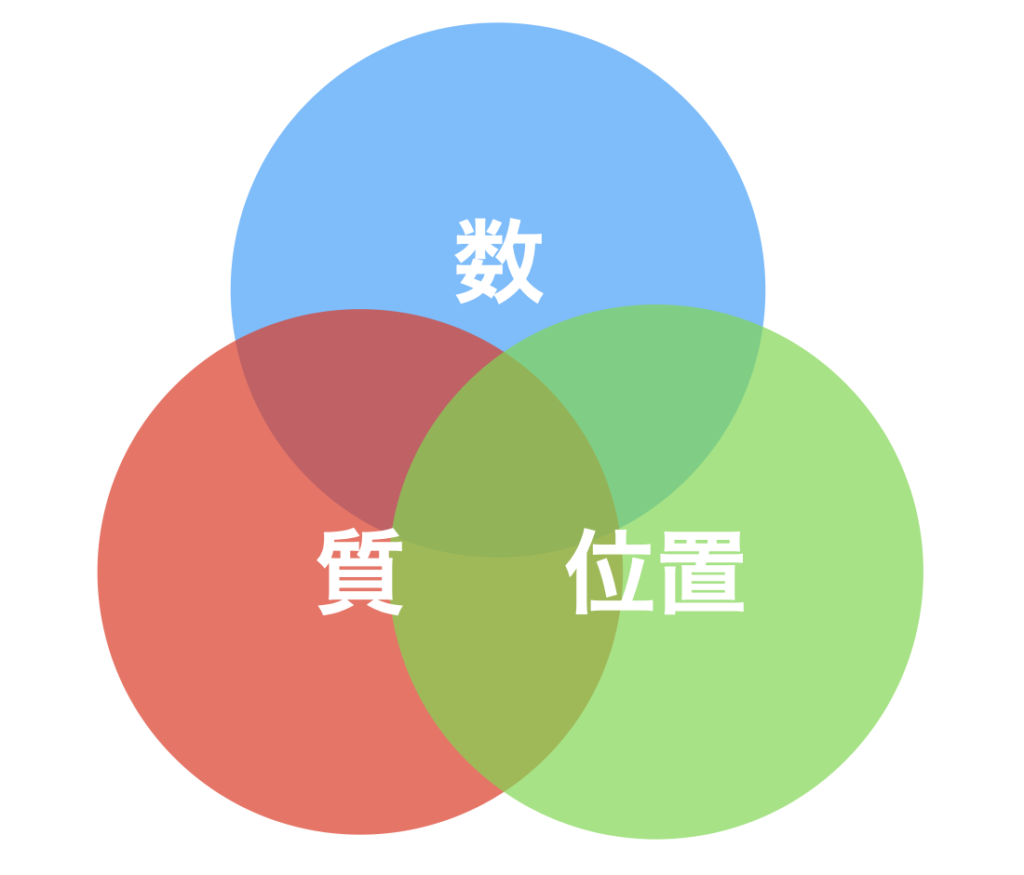
In chess, the concept of “positional play” has long been understood, where tactics arise from three types of advantages based on the arrangement of pieces (position) at any stage of the game, determining the outcome.
This concept has been applied to modern soccer and, of course, can also be applied to futsal.
Let’s explain each of the three advantages one by one.
- Numerical superiority
- Qualitative superiority
- Positional superiority
Numerical Superiority
Numerical superiority, as the name suggests, is when the number of players in a certain zone from your team exceeds that of the opposing team, creating an advantage. In chess, this is referred to as quantitative superiority.
This advantage is particularly evident in transitions and power plays.
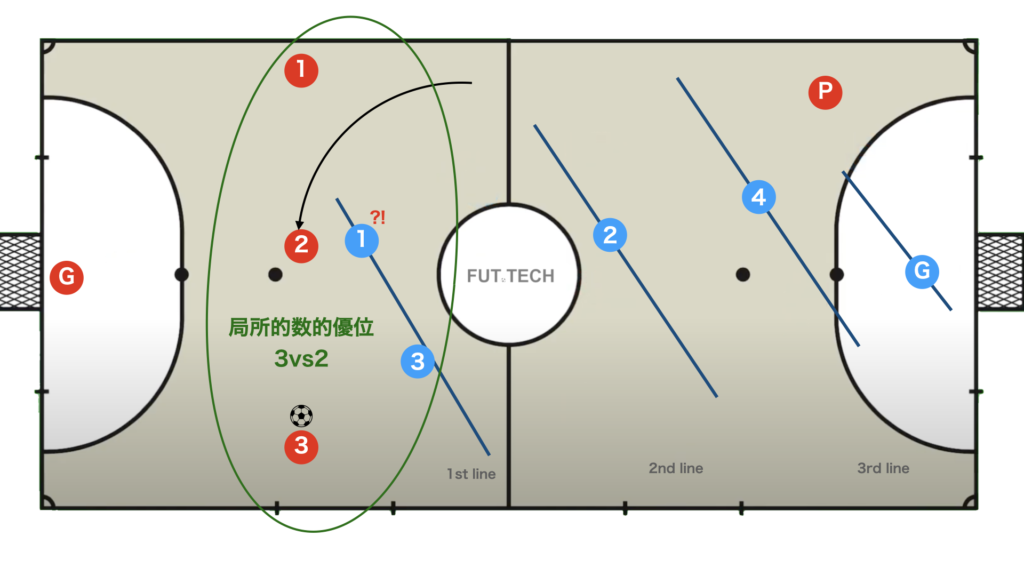
In set attacks, as shown in the figure above, numerical superiority can occur in a certain zone (the first row) when the second-row players make line cuts.
This kind of numerical superiority in a specific zone is called local numerical superiority.
Qualitative Superiority

Qualitative superiority refers to the advantage of individual abilities over the opponent.
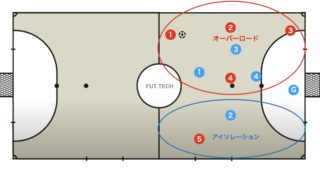
The isolation tactic, which isolates a skilled dribbler, is particularly a strategy that leverages qualitative superiority.
The individual abilities contributing to qualitative superiority can be broadly classified into four categories.
- Technique
- Physical
- Intelligence
- Mental
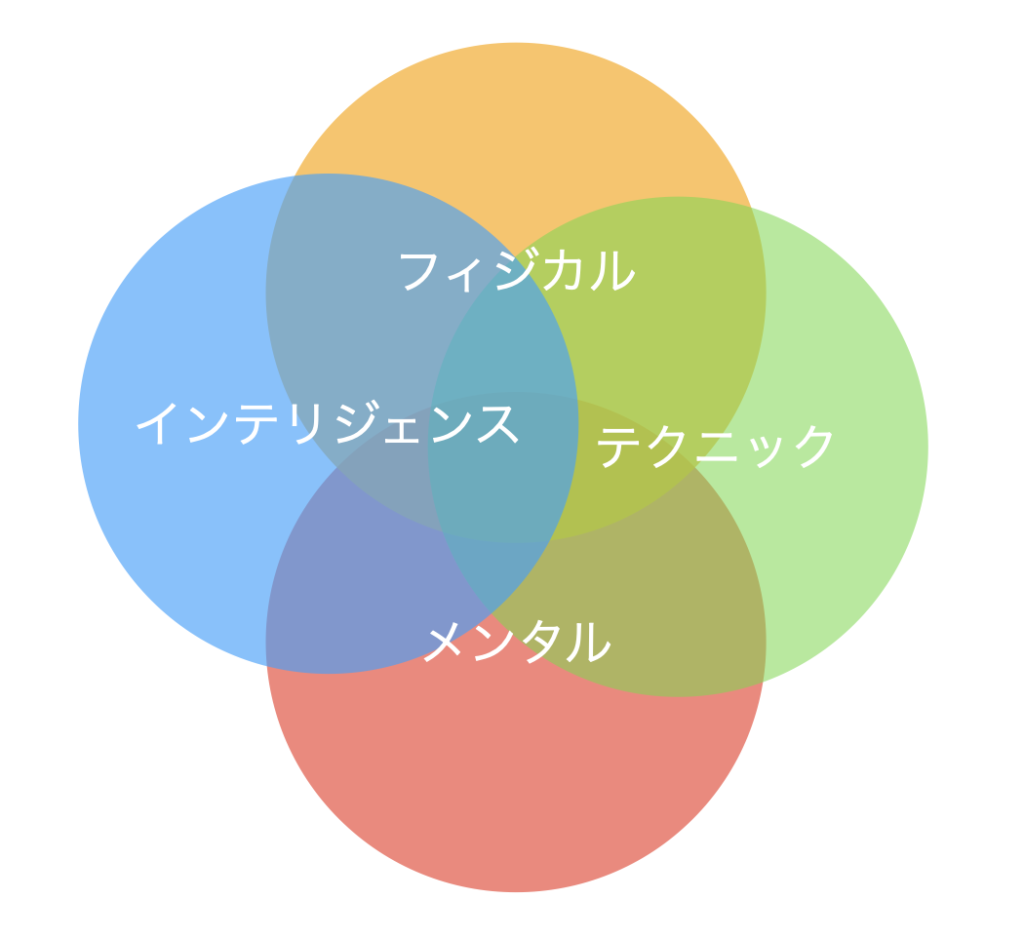
Technique
Technique refers to the foot skills a player uses to handle the ball.
- Trap
- Pass
- Dribble
- Shoot
It’s important to incorporate each technique into your body while understanding them theoretically, and sometimes considering the laws of physics can simplify understanding. Moreover, technique is also influenced by physical abilities, which will be explained later.
Physical
Physical refers to the bodily or physical aspects of a player.
- Speed (speed, agility, explosive power)
- Power (weight, inner muscle, outer muscle)
- Length of limbs, height
Weight might be underestimated, but in conclusion, it’s generally better to be heavier.
Considering the second law of motion, ma=F, it’s clear that a heavier weight allows for transmitting power with less acceleration.
Therefore, heavier individuals tend to have stronger shots and are more formidable in ball contests.
However, weight and agility tend to be inversely proportional, so it’s important to be cautious about gaining too much weight.
Intelligence
Intelligence refers to the mental processes, IQ, vision, etc., that contribute to a player’s understanding of tactics and ability to make decisions in a short amount of time.
It’s not just about understanding and embodying the team’s play model but also about the ability to perceive and make appropriate decisions quickly.
The ability to perceive is not just about the brain but also about vision (dynamic vision, static vision), so some club teams also conduct training to broaden their field of vision.
Mental
Mental refers to the psychological state.
Although it might seem similar to intelligence, mental state is greatly influenced by the day’s condition, the atmosphere of the match venue, and the situation, and can sometimes affect physical and intelligence aspects, making it a crucial element.
Mental is the most difficult element to improve and is heavily influenced by a person’s experiences and upbringing.
Some professional players even have a psychologist or a sports mental specialist as a personal counselor to help them perform at their best.
Recently, mental training through meditation and mindfulness, focusing on the present moment, has begun to be applied to sports.
Positional Superiority
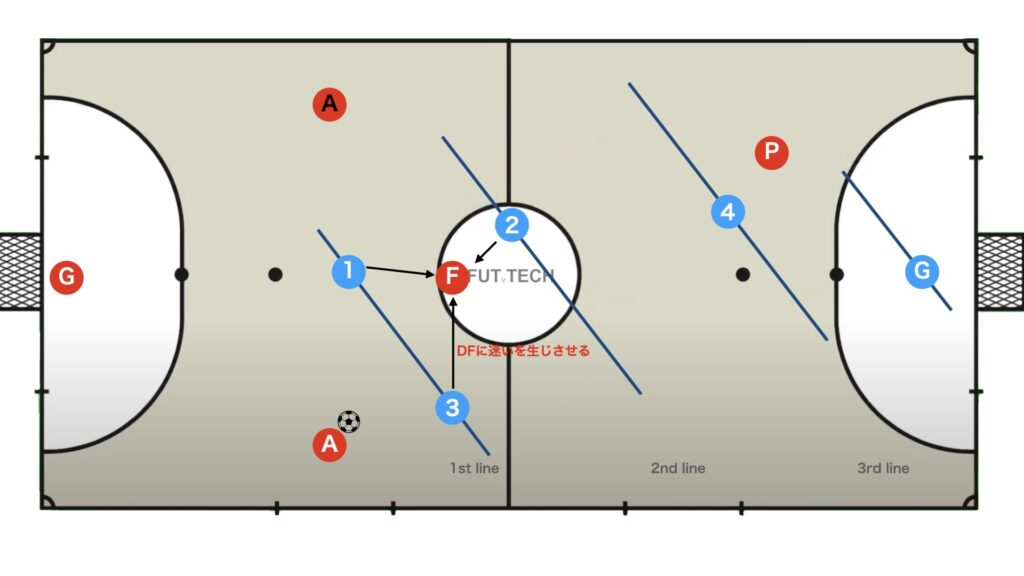
Positional superiority is the advantage gained by taking positions that confuse the opponent or are undesirable for them, and by the orientation of the body.
In futsal, it refers to maneuvering in the opponent’s blind spots or behind them, or positioning oneself to receive the ball between the lines of the opponent’s defense.
Even if you receive the ball in the same position, the advantage changes depending on the orientation of your body.
As a result, positional superiority often leads to numerical superiority.
Positional Play Pursuing the Three Advantages
Pep Guardiola, who has managed Bayern Munich and Manchester City, applies the concept of positional play (positional theory) to football (soccer) as a means to create the three advantages.
Positional theory is the concept of considering who to place where and in which direction, and how to enhance the three advantages to achieve tactical (social) superiority.
Especially important here is the concept of “Who to place?”
For example, in futsal, when adopting a 3-1 formation, whether you place a player who is good at holding up play or a smaller player with good foot skills in the front makes a big difference.
Thus, it’s crucial to strongly consider who to place in each position.
Some people in soccer refer to the general term for positioning and play that enhances positional advantage against the opponent’s defense as positional play. Definitions vary among individuals, but this blog considers the concept of deciding who to place where and in which direction as positional play.
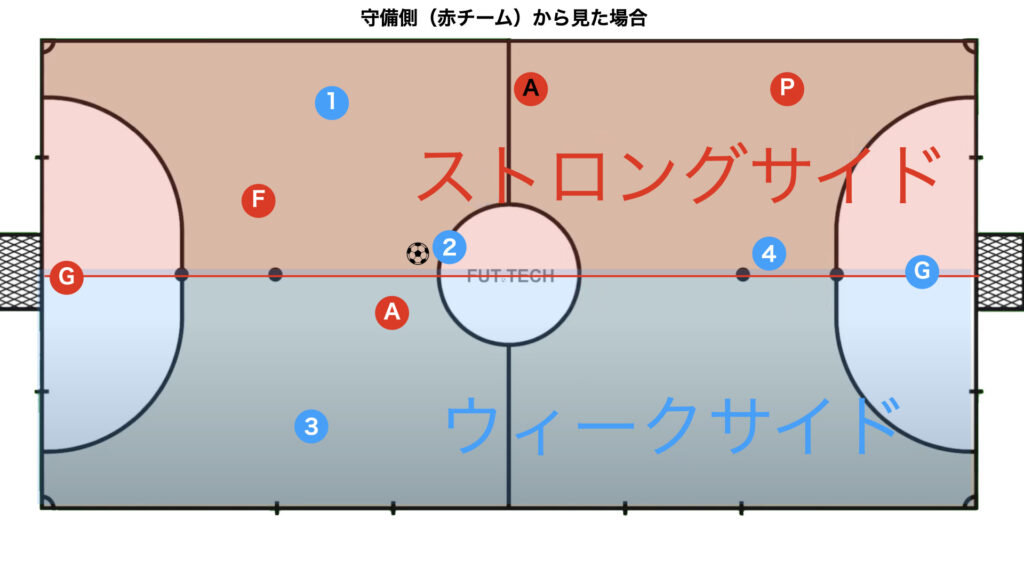
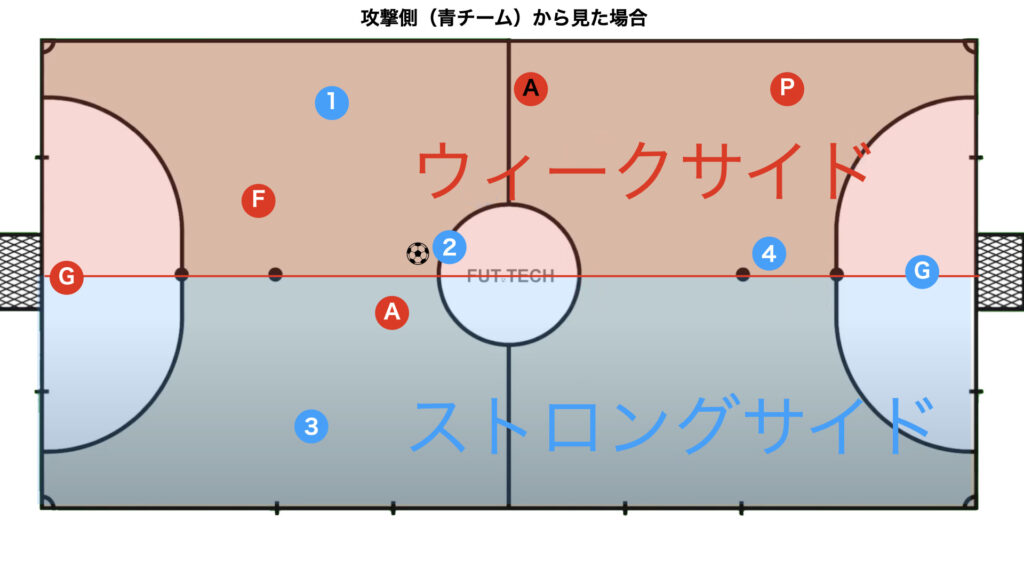
The Strong Side and Weak Side are Two Sides of the Same Coin
The strong side and weak side are subjectively determined by one team, so if you switch the perspective of offense and defense (your team and the opposing team), the strong side and weak side are reversed.
In other words, the strong side for the attacking team becomes the weak side for the defending team, and vice versa, the weak side for the attacking team becomes the strong side for the defending team.
This concept is very important to understand, otherwise, it becomes unclear which side the terms strong side and weak side refer to.
This concept is emphasized in transition phases, so we present diagrams for transitions.
From the Defender’s Perspective
From the Attacker’s Perspective
Summary
This time, we explained the three advantages that are important to consider when thinking about the strong side and weak side.
It might have felt a bit abstract and difficult, but these are important concepts to understand when considering play models or analyzing games.
It’s important to consider the three advantages (numerical superiority, qualitative superiority, positional superiority) when thinking about the strong side and weak side.
The strong side and weak side are two sides of the same coin.
We hope this article provides hints for your team to score more goals (checkmate).